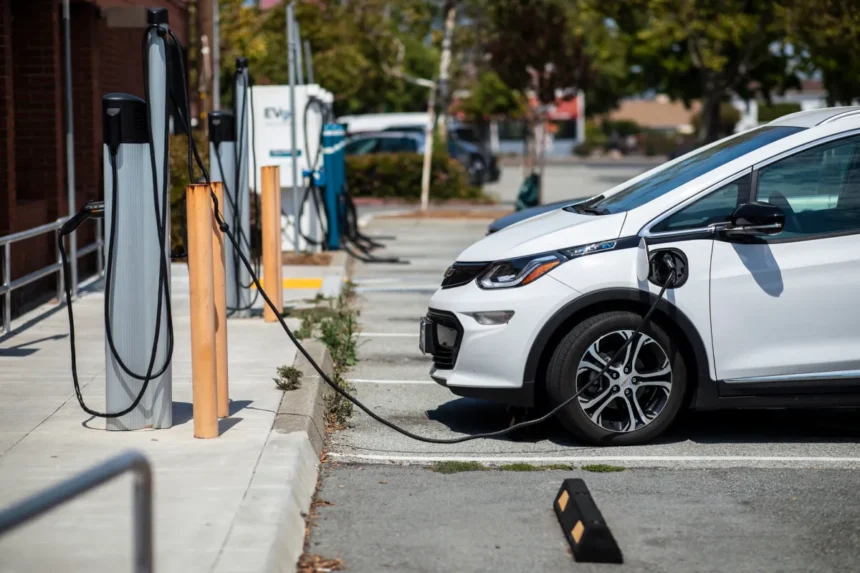
Electric cars are gaining immense popularity, not just because they are environmentally friendly but also due to the advancements in technology that make them more practical and cost-effective. As the world moves toward sustainable solutions, electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming the go-to option for many drivers. But have you ever wondered what makes an electric car tick? What are the key parts that drive this innovative technology?
In this blog post, we will take a deep dive into the essential components of an electric car, explaining how each part functions to make these vehicles a practical alternative to traditional gas-powered cars. Whether you’re considering buying an electric car or are just curious about how they work, this guide will give you a thorough understanding of electric car parts and their functions.
The Basic Components of an Electric Car
An electric car is fundamentally different from a conventional car because it operates on electricity stored in batteries rather than relying on internal combustion engines (ICE). However, despite this difference, electric vehicles still share many components with traditional cars, including wheels, doors, and seats. The major differences lie in the powertrain, battery systems, and various electrical systems that keep the car running smoothly.
Here are the core components of an electric car:
- Electric Motor
- Battery Pack
- Power Electronics
- Onboard Charger
- Drivetrain
- Thermal Management System
- Regenerative Braking System
- Charging Port
- Infotainment System and Software
Now, let’s break down each of these components and explore how they contribute to the functioning of an electric car.
1. Electric Motor: The Heart of an Electric Car
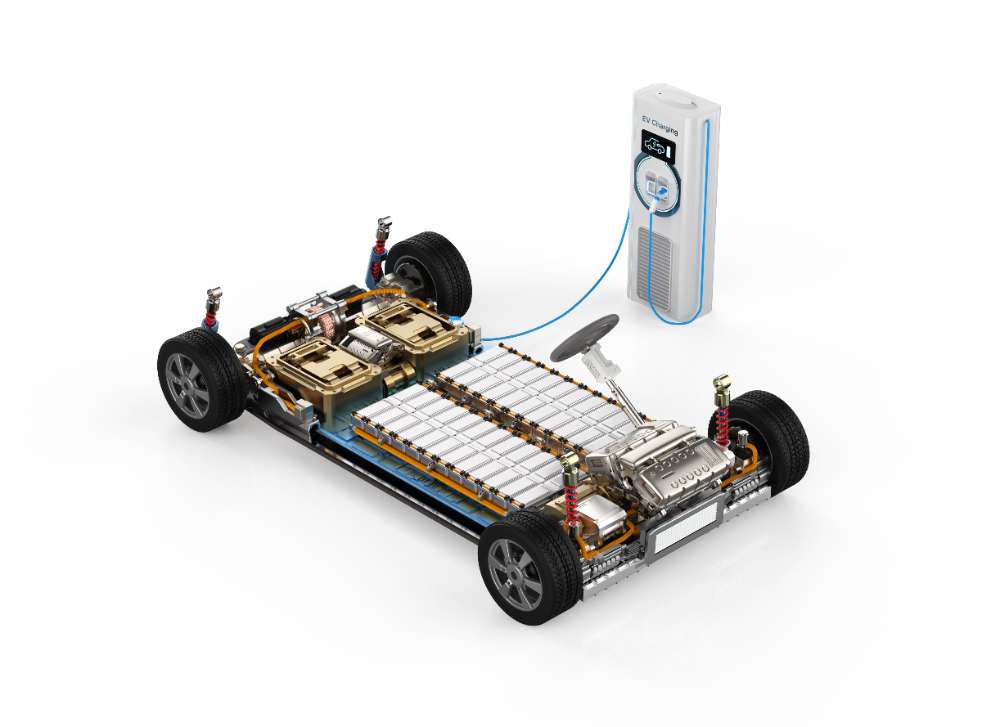

The electric motor is one of the most critical components of an electric vehicle (EV). Unlike conventional cars, which rely on a gasoline engine to generate power, electric cars use an electric motor to turn the wheels. This motor is powered by electricity from the vehicle’s battery pack, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle.
Electric motors used in EVs are typically either AC (Alternating Current) or DC (Direct Current) motors. However, the most common type used in electric cars is the AC induction motor. The motor is lightweight, efficient, and has fewer moving parts compared to an internal combustion engine. This makes electric motors more reliable and cheaper to maintain.
There are various types of electric motors, but the most common ones used in electric cars include:
- AC Induction Motor (Squirrel Cage)
- Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM)
- Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM)
The key advantages of electric motors include instant torque, smooth acceleration, and quiet operation. They don’t require transmissions, unlike traditional engines, because the motor can provide a wide range of speeds directly from a standstill.
2. Battery Pack: The Power Source
When it comes to electric cars, the battery pack is the heart of the powertrain. Without a proper battery system, an EV wouldn’t function. The battery pack stores the electrical energy required to power the motor and other components of the vehicle. Electric car batteries are usually made from lithium-ion (Li-ion) or lithium-polymer (LiPo) technology because these types of batteries offer the best combination of power, range, and weight.
Battery packs come in different sizes depending on the vehicle model and the range it is designed for. For example, the Tesla Model S has battery packs that can store between 60 kWh and 100 kWh of energy, allowing it to travel over 300 miles on a single charge.
The battery pack is usually located at the bottom of the vehicle, which helps improve the car’s center of gravity and stability. Modern electric vehicle batteries are designed to be highly efficient and last for many years with proper care. As technology advances, we can expect even higher energy densities, faster charging times, and more efficient battery management systems.
3. Power Electronics: Managing Electricity Flow
Power electronics are a critical part of the electric car, helping manage the flow of electricity between the battery and the motor. These components are responsible for controlling the power output to the electric motor, ensuring it gets the right amount of electricity at the right time.
Key power electronic components include:
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC (direct current) power stored in the battery into AC (alternating current) power required by the electric motor.
- DC-DC Converter: This component ensures that the high-voltage battery can also power the low-voltage systems like lights, infotainment, and climate control.
- Controller: The controller regulates the motor’s speed and torque based on input from the accelerator pedal.
Power electronics are essential for the efficient operation of electric vehicles, helping to ensure the system operates at peak performance while keeping energy losses to a minimum.
4. Onboard Charger: Recharging the Battery
Electric vehicles require recharging to keep the battery charged and ready to drive. The onboard charger is responsible for converting the AC power from the electrical grid into DC power that can be stored in the vehicle’s battery. This charger is built directly into the car, making it convenient for owners to plug into any standard electrical outlet.
The onboard charger’s capacity determines how quickly the vehicle can recharge. Modern EVs can typically be recharged in hours using home charging stations, while high-capacity chargers at public stations can recharge a vehicle to 80% in less than 30 minutes.
5. Drivetrain: Power Transfer System
The drivetrain in an electric car is the system that transmits power from the electric motor to the wheels. In most electric cars, the drivetrain is simpler than traditional vehicles. While traditional vehicles have a transmission that shifts gears, electric cars often have a single-speed transmission or no transmission at all.
This is because electric motors can provide full torque at any speed, eliminating the need for gear shifting. The drivetrain consists of the motor, the power electronics, and the axle that connects to the wheels. In some electric cars, a differential may also be present, especially for vehicles with dual motors (one for each axle).
6. Thermal Management System: Keeping It Cool
One of the challenges of electric vehicles is managing the heat generated by the battery pack and electric motor. As with any electronic device, batteries and motors can overheat if not properly cooled, which could lead to poor performance or even damage.
The thermal management system in an electric car is responsible for regulating the temperature of the battery, motor, and power electronics. This system uses liquid cooling, fans, and heat exchangers to ensure that the vehicle’s critical components stay within the optimal temperature range, which improves the car’s performance and longevity.
7. Regenerative Braking System: Efficient Energy Recovery
One of the most innovative features of electric cars is the regenerative braking system. This system allows the electric car to recover energy during braking and send it back to the battery for later use.
When you press the brake pedal in an electric vehicle, the motor switches into reverse, acting as a generator and converting kinetic energy into electrical energy. This process slows down the car and helps recharge the battery, increasing the overall efficiency of the vehicle.
Regenerative braking reduces wear on traditional braking components and extends the life of the vehicle’s brake pads. It also improves energy efficiency, which is crucial for increasing the vehicle’s range.
8. Charging Port: Access to Power
The charging port is where you plug the car into an electrical source to recharge the battery. There are different types of charging ports depending on the car’s make and the charging standard used in the region. For instance, some electric cars use the Type 1 or Type 2 connectors, while others may use CHAdeMO or CCS (Combined Charging System) fast-charging ports.
Charging ports vary in speed, from Level 1 (standard home outlet) to Level 2 (faster home or public charging stations) and DC fast charging stations. The faster the charging rate, the quicker the vehicle can be fully charged.
9. Infotainment System and Software: Connecting the Driver
Modern electric cars are equipped with sophisticated infotainment systems that offer connectivity, navigation, and entertainment. These systems are often integrated with the car’s software, which controls everything from the battery’s performance to the driving experience.
Electric car manufacturers, such as Tesla, have developed user-friendly touchscreens that provide real-time data on energy usage, range, and charging status. These infotainment systems are also linked to mobile apps, allowing drivers to monitor their vehicle remotely, plan trips based on charging station locations, and even pre-condition the car for optimal range.
Conclusion
Electric cars are revolutionizing the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional gas-powered vehicles. By understanding the essential parts and how they work, you can appreciate the complexity and innovation behind every electric vehicle on the road today. From the electric motor that drives the car to the battery pack that powers it, each component plays a vital role in ensuring that electric cars are not only eco-friendly but also reliable, efficient, and enjoyable to drive.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more improvements in electric car parts and performance. The future of transportation is electric, and understanding the inner workings of these vehicles is the first step toward embracing the future of mobility.
If you’re interested in learning more about electric cars, be sure to check out our other articles on EV technology, charging infrastructure, and the environmental benefits of switching to an electric vehicle.